Pipe Syntax Conversion
Convert between standard SQL and BigQuery's pipe syntax.
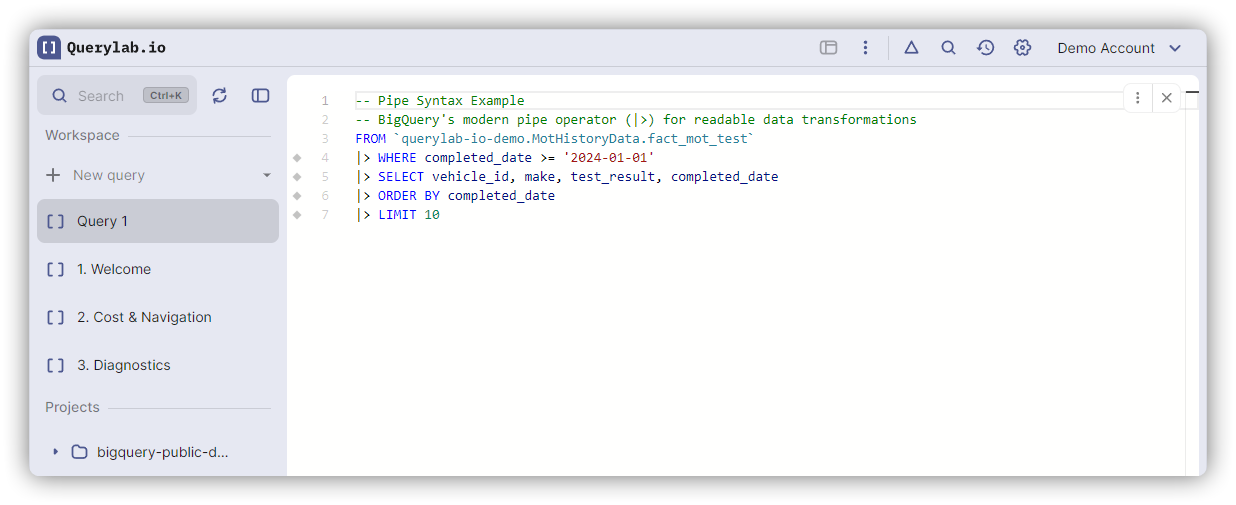
What is Pipe Syntax?
A linear, data-flow oriented way to write SQL using the |> operator.
Standard SQL:
SELECT user_id, COUNT(*) AS orders
FROM orders
WHERE status = 'completed'
GROUP BY user_id
ORDER BY orders DESC;
Pipe Syntax:
FROM orders
|> WHERE status = 'completed'
|> AGGREGATE COUNT(*) AS orders GROUP BY user_id
|> ORDER BY orders DESC;
Pipe syntax reads top-to-bottom in execution order.
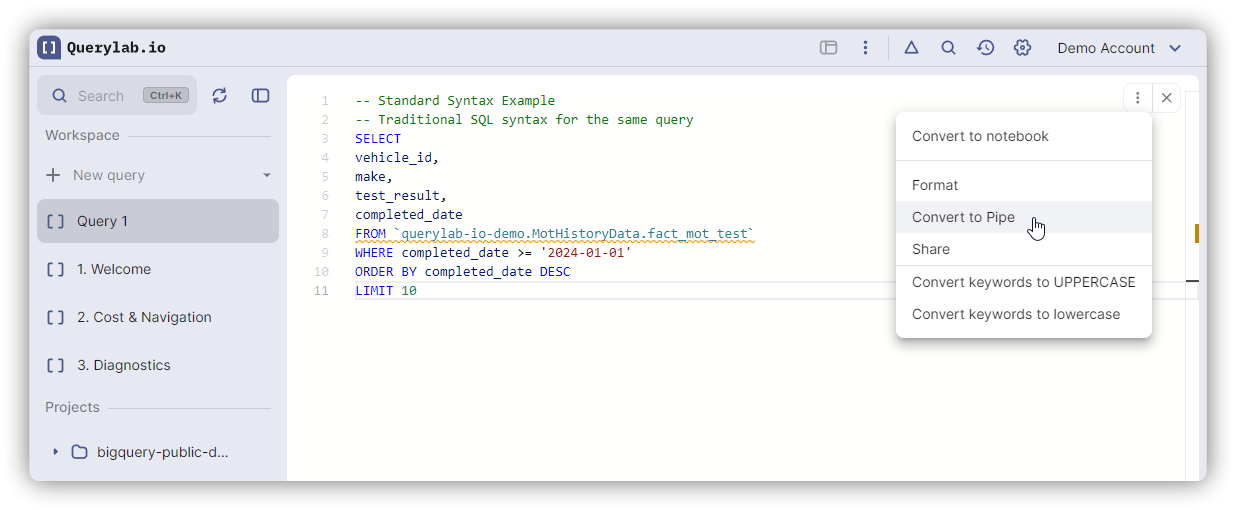
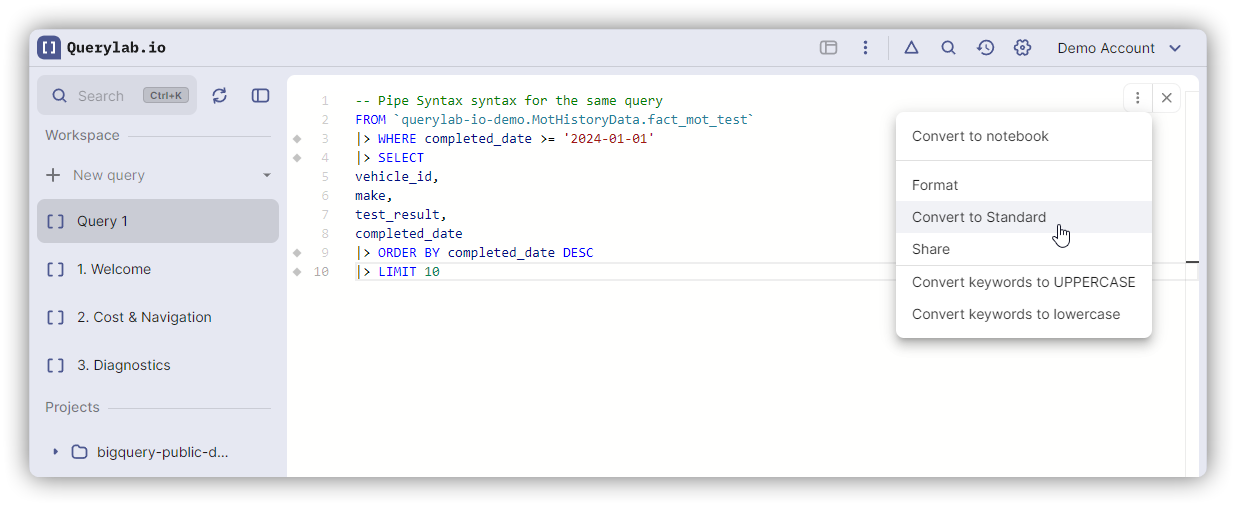
Conversion Shortcuts
| Action | Mac | Windows/Linux |
|---|---|---|
| Convert to Pipe | Cmd+Alt+P | Ctrl+Alt+P |
| Convert to Standard | Cmd+Alt+S | Ctrl+Alt+S |
Works on full document or selection.
Pipe Operations
| Standard SQL | Pipe Syntax |
|---|---|
SELECT cols FROM table | FROM table |> SELECT cols |
WHERE condition | |> WHERE condition |
GROUP BY cols + aggregates | |> AGGREGATE ... GROUP BY cols |
HAVING condition | |> WHERE condition (after AGGREGATE) |
JOIN table ON ... | |> JOIN table ON ... |
ORDER BY cols | |> ORDER BY cols |
LIMIT n | |> LIMIT n |
TABLESAMPLE SYSTEM (n PERCENT) | |> TABLESAMPLE SYSTEM (n PERCENT) |
PIVOT(agg FOR col IN (...)) | |> PIVOT(agg FOR col IN (...)) |
UNPIVOT(val FOR name IN (...)) | |> UNPIVOT(val FOR name IN (...)) |
ML.PREDICT(MODEL m, TABLE t) | FROM t |> CALL ML.PREDICT(MODEL m) |
WINDOW w AS (PARTITION BY col) | |> WINDOW w AS (PARTITION BY col) |
AS alias | |> AS alias |
UNION ALL | |> UNION ALL (...) |
INTERSECT DISTINCT | |> INTERSECT DISTINCT (...) |
EXCEPT DISTINCT | |> EXCEPT DISTINCT (...) |
Pipe-Only: EXTEND
Add computed columns without listing all existing columns.
FROM users
|> EXTEND UPPER(name) AS name_upper;
Keeps all columns and adds name_upper.
Mixed Syntax
BigQuery supports mixing standard and pipe syntax in the same query.
WITH cleaned AS (
FROM raw_events
|> WHERE event_date >= '2024-01-01'
|> SELECT user_id, event_type
),
stats AS (
SELECT user_id, COUNT(*) AS count
FROM cleaned
GROUP BY user_id
)
SELECT * FROM stats;
Set Operations
UNION, INTERSECT, and EXCEPT are fully supported in pipe syntax:
-- Standard SQL
SELECT id FROM users UNION ALL SELECT id FROM admins
-- Converts to Pipe Syntax
FROM users
|> SELECT id
|> UNION ALL (FROM admins |> SELECT id)
Table Sampling
Sample data for faster exploration or cost reduction:
FROM large_table
|> TABLESAMPLE SYSTEM (10 PERCENT)
|> SELECT *
Supports PERCENT, ROWS, and REPEATABLE seed for reproducibility.
PIVOT and UNPIVOT
Transform rows to columns and vice versa:
-- PIVOT: Rows to columns
FROM sales
|> PIVOT(SUM(revenue) FOR quarter IN ('Q1', 'Q2', 'Q3', 'Q4'))
-- UNPIVOT: Columns to rows
FROM quarterly_data
|> UNPIVOT(revenue FOR quarter IN (Q1, Q2, Q3, Q4))
UNPIVOT supports INCLUDE NULLS and EXCLUDE NULLS modifiers.
ML Functions (CALL)
Call table-valued functions like BigQuery ML:
-- Pipe syntax
FROM input_data
|> CALL ML.PREDICT(MODEL `project.dataset.model`)
-- Converts to standard SQL
SELECT * FROM ML.PREDICT(MODEL `project.dataset.model`, TABLE(input_data))
Works with ML.PREDICT, ML.GENERATE_TEXT, ML.FORECAST, and custom TVFs.
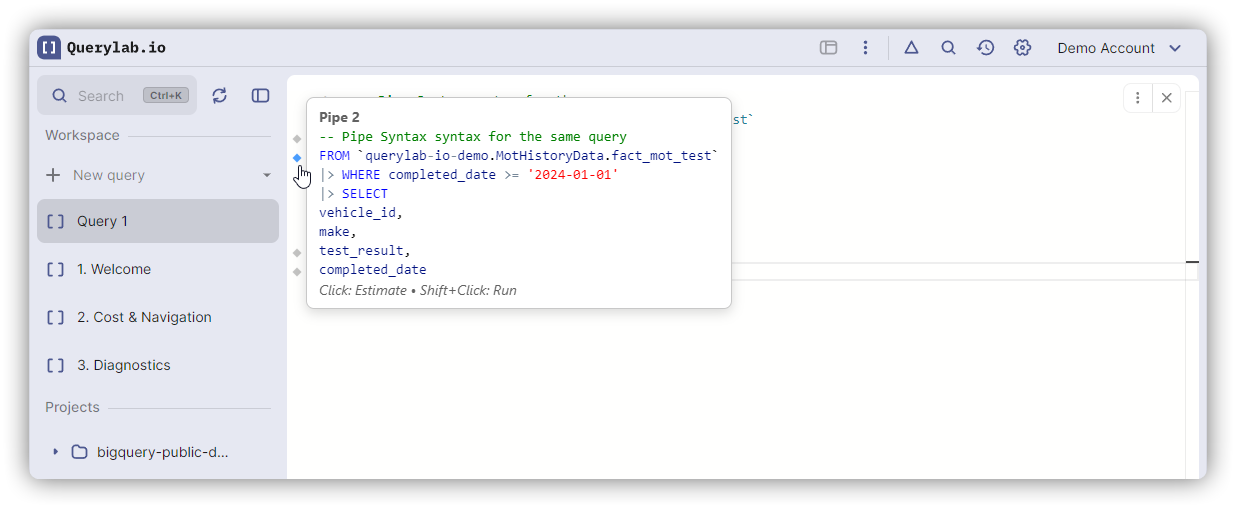
Debugging with Partial Execution
Pipe syntax works with Partial Execution - each |> shows a gutter icon. Shift+Click any pipe operator to execute up to that stage and inspect intermediate results.
Limitations
- SELECT without FROM cannot convert to pipe (pipe requires FROM)
- MATCH_RECOGNIZE cannot convert to pipe (BigQuery limitation - use standard SQL)
- Use partial conversion (select portion, then convert) for complex queries